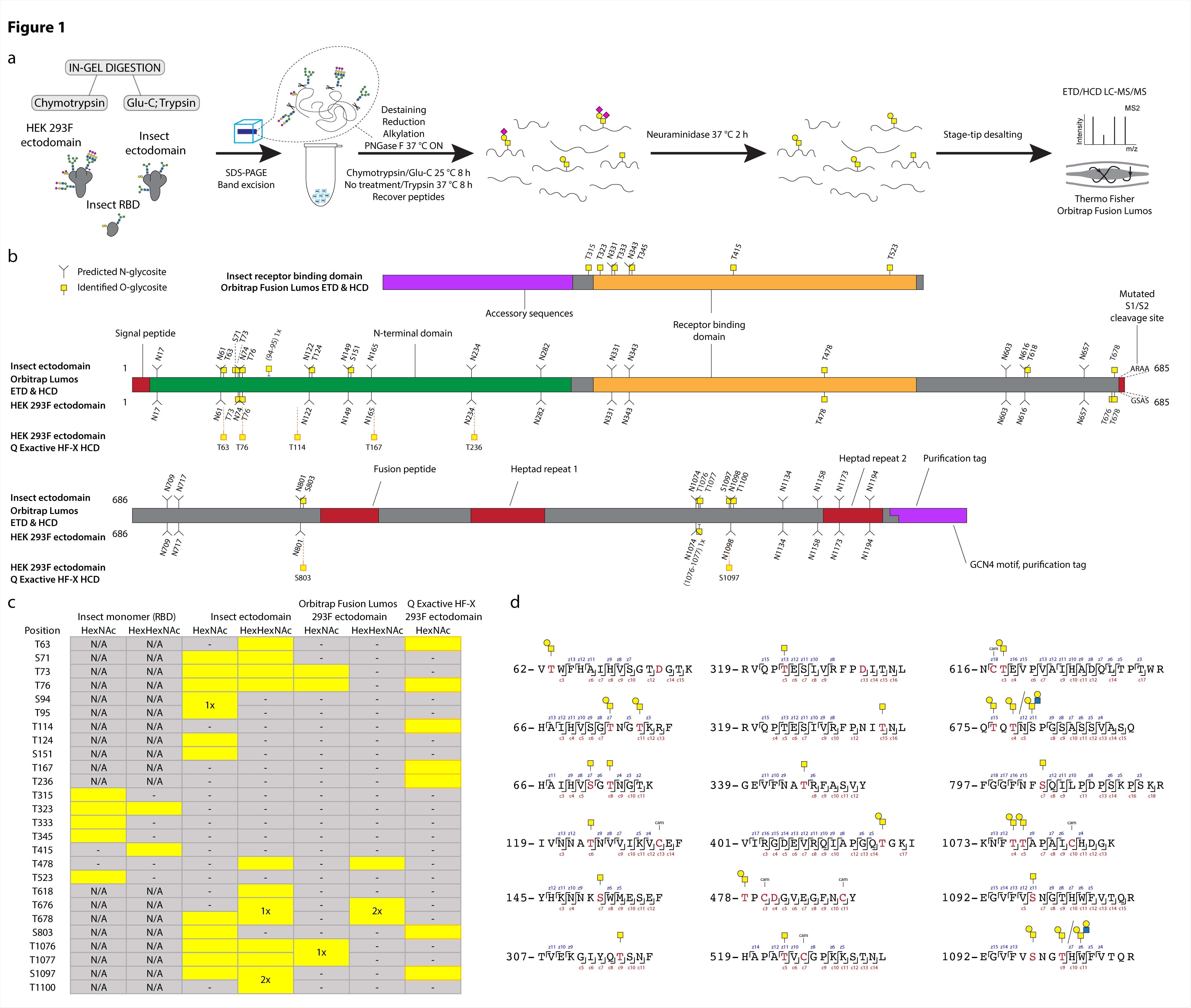
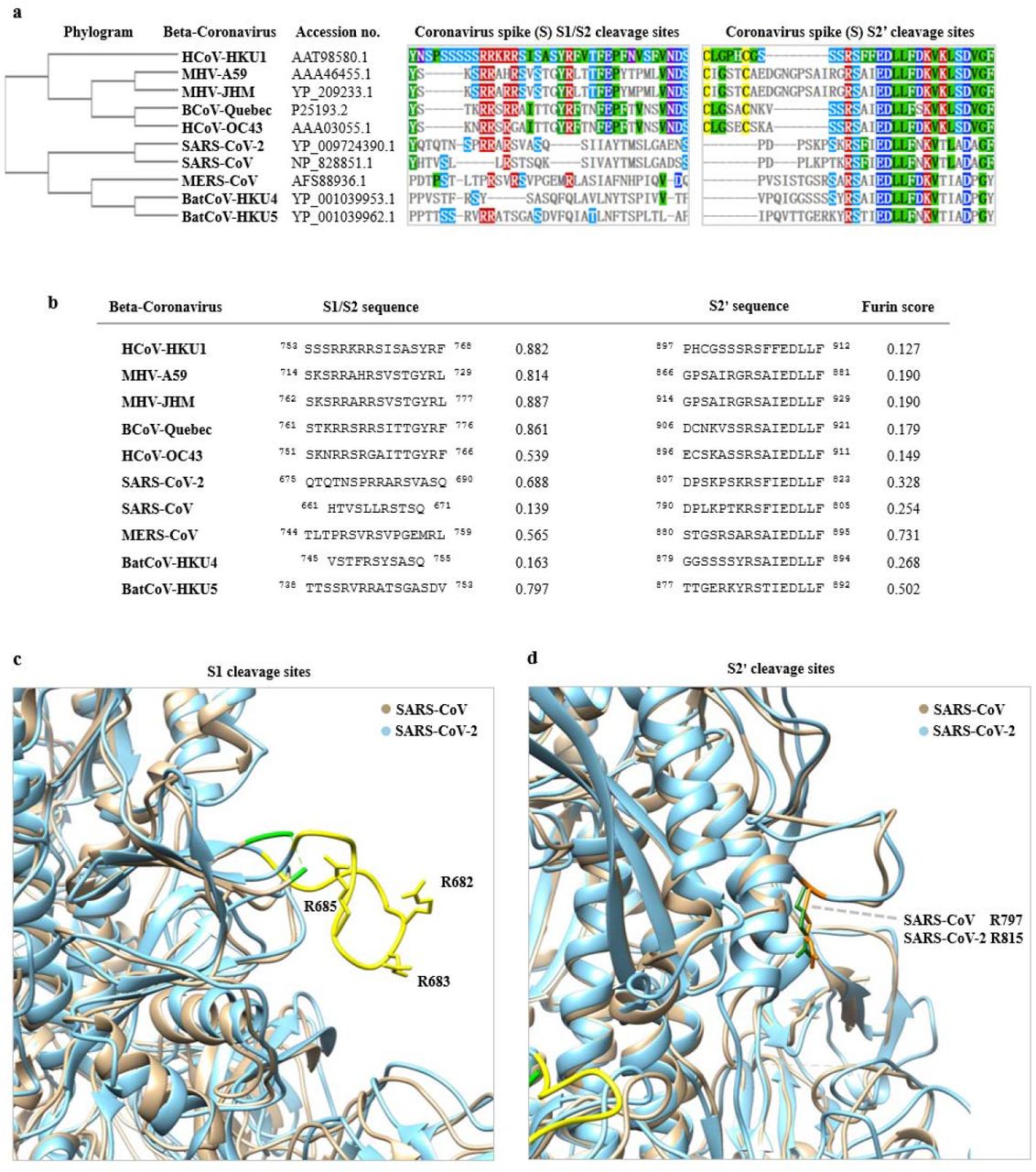
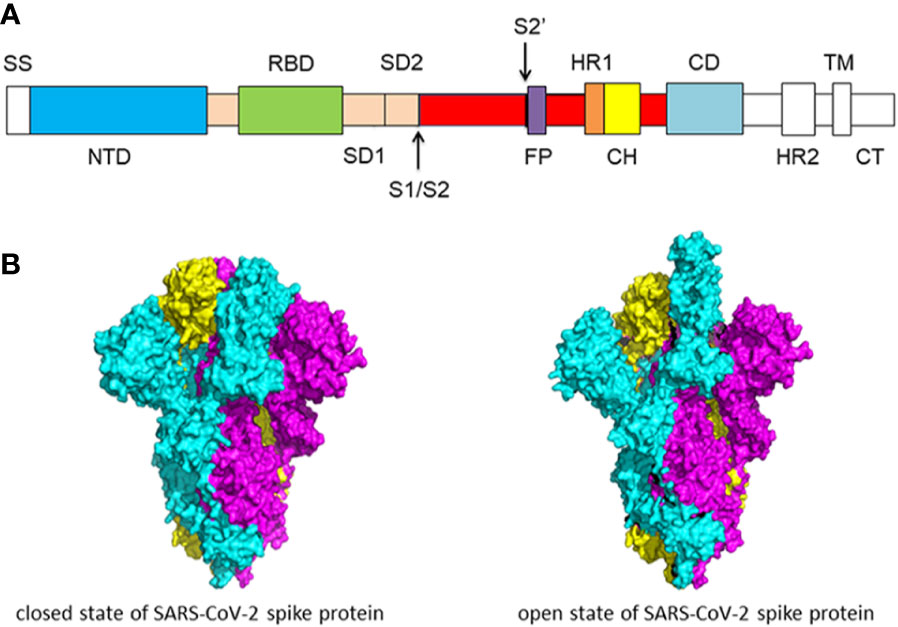
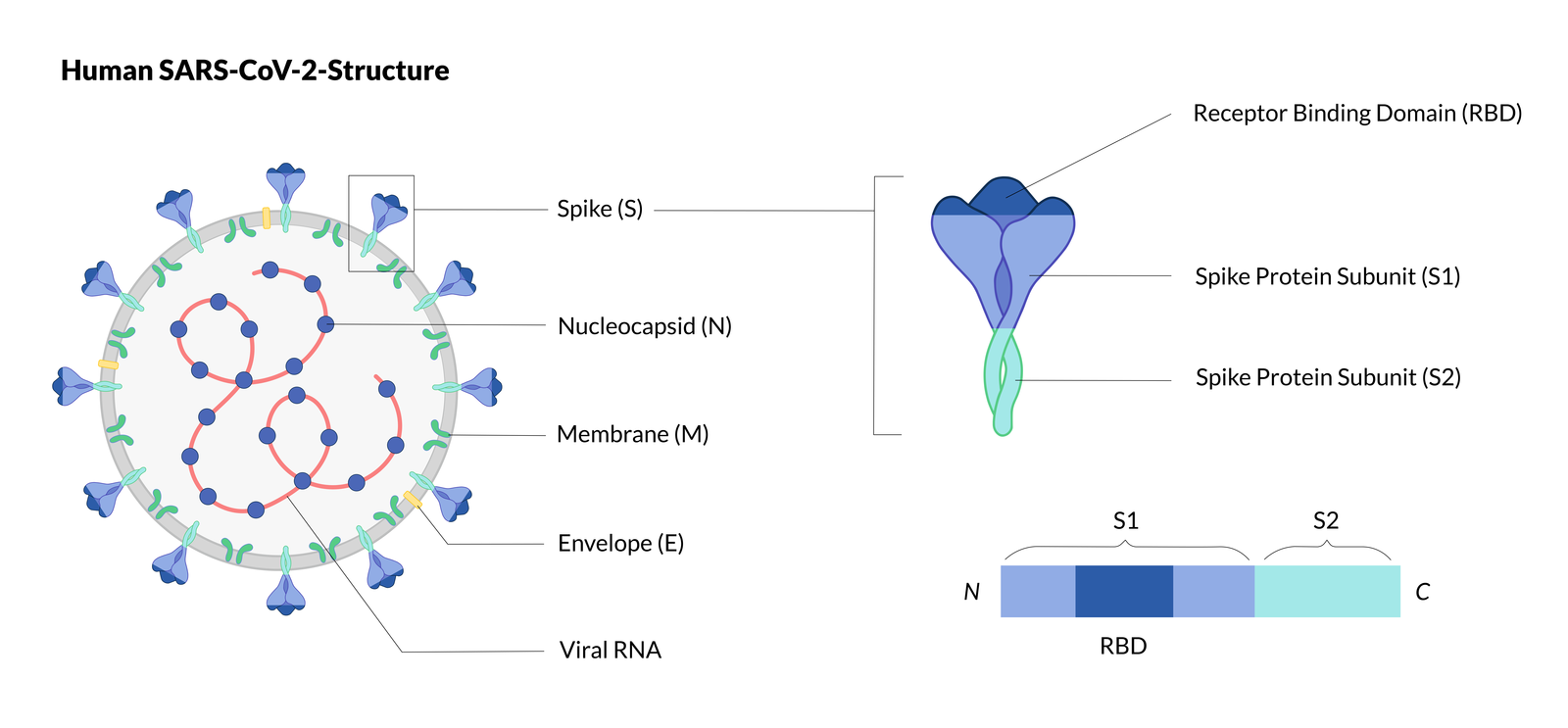
Gene of the month: the 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2 novel coronavirus spike protein | Journal of Clinical Pathology

Three Amino Acid Changes in Avian Coronavirus Spike Protein Allow Binding to Kidney Tissue | Journal of Virology
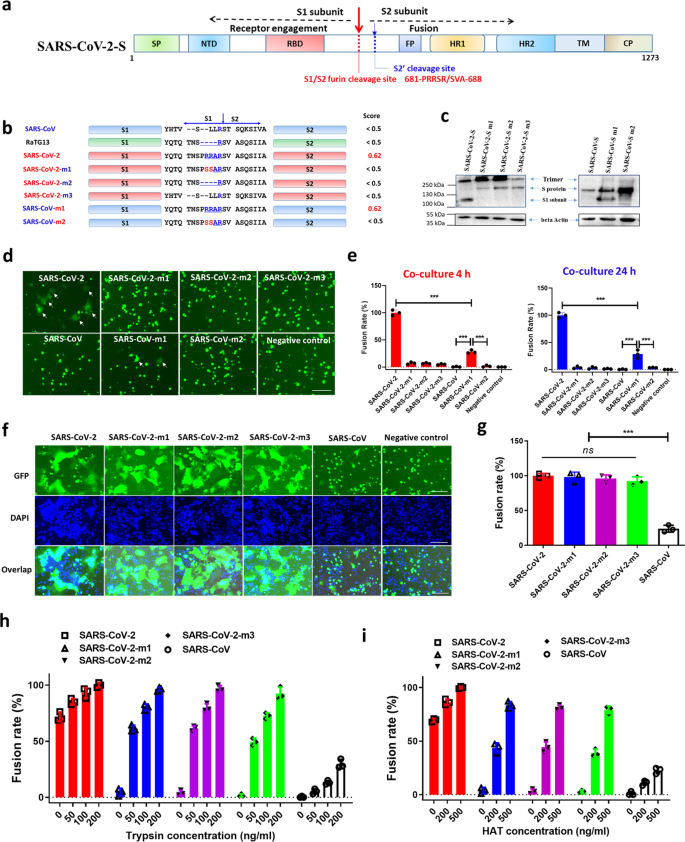
The role of furin cleavage site in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated membrane fusion in the presence or absence of trypsin | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
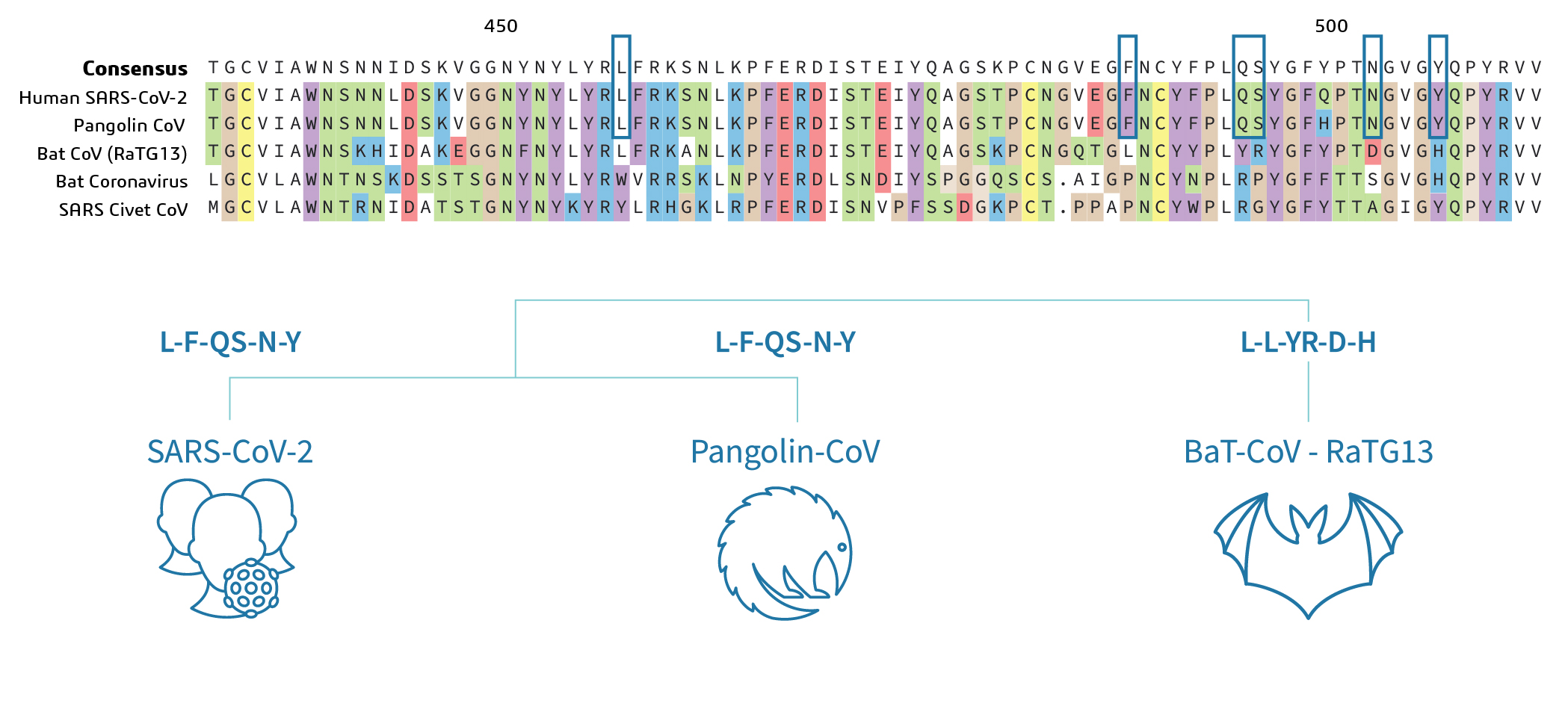
nCoV-2019 Spike Protein Receptor Binding Domain Shares High Amino Acid Identity With a Coronavirus Recovered from a Pangolin Viral Metagenomic Dataset - nCoV-2019 Evolutionary History - Virological
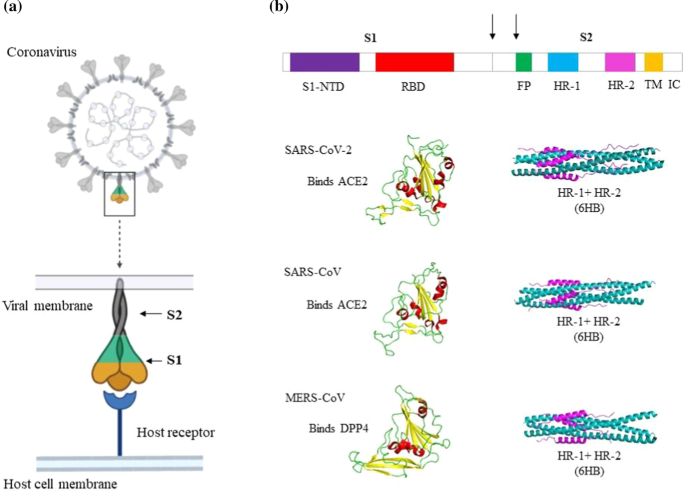
A comparative study of human betacoronavirus spike proteins: structure, function and therapeutics | SpringerLink
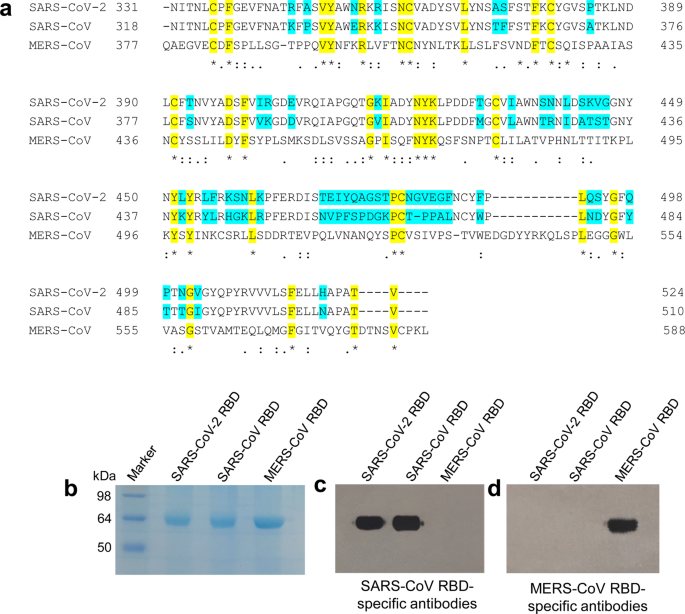
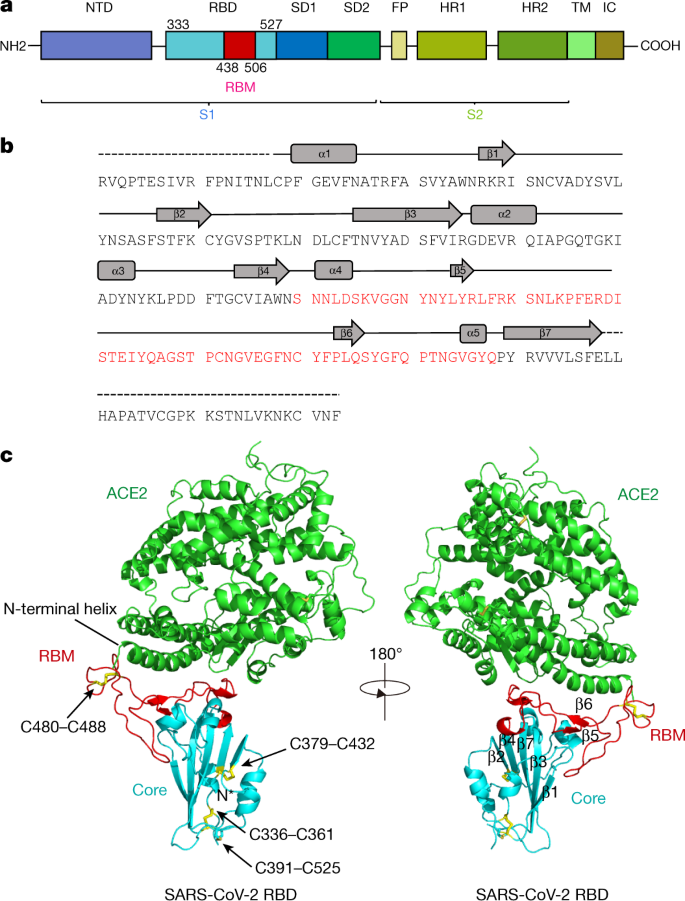
Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine | Cellular & Molecular Immunology

A Multibasic Cleavage Site in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Is Essential for Infection of Human Lung Cells - ScienceDirect
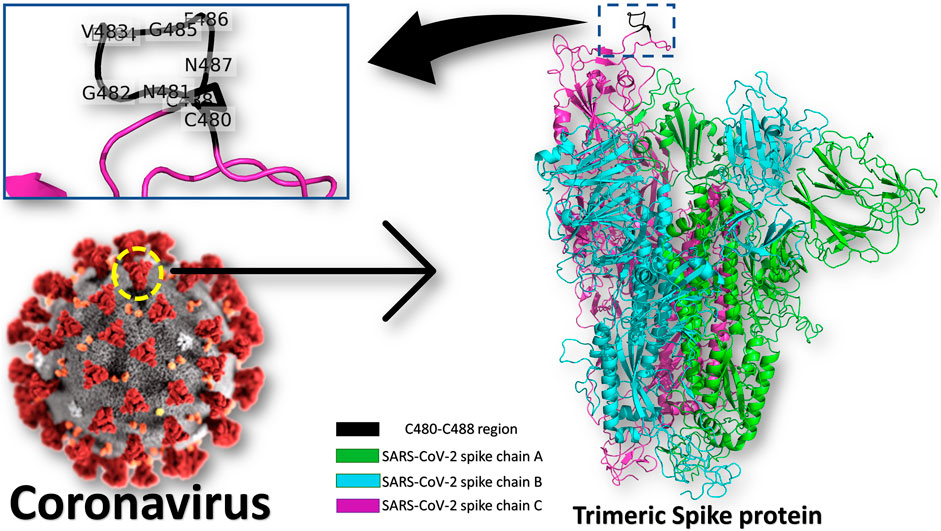
Frontiers | SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Heat Shock Protein A5 (GRP78) Recognition may be Related to the Immersed Human Coronaviruses

SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Antibody evasion and cryo-EM structure of spike protein–ACE2 complex | Science
Cureus | Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Activation, p53, and Autophagy Inhibition Characterize the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein Induced Neurotoxicity | Article
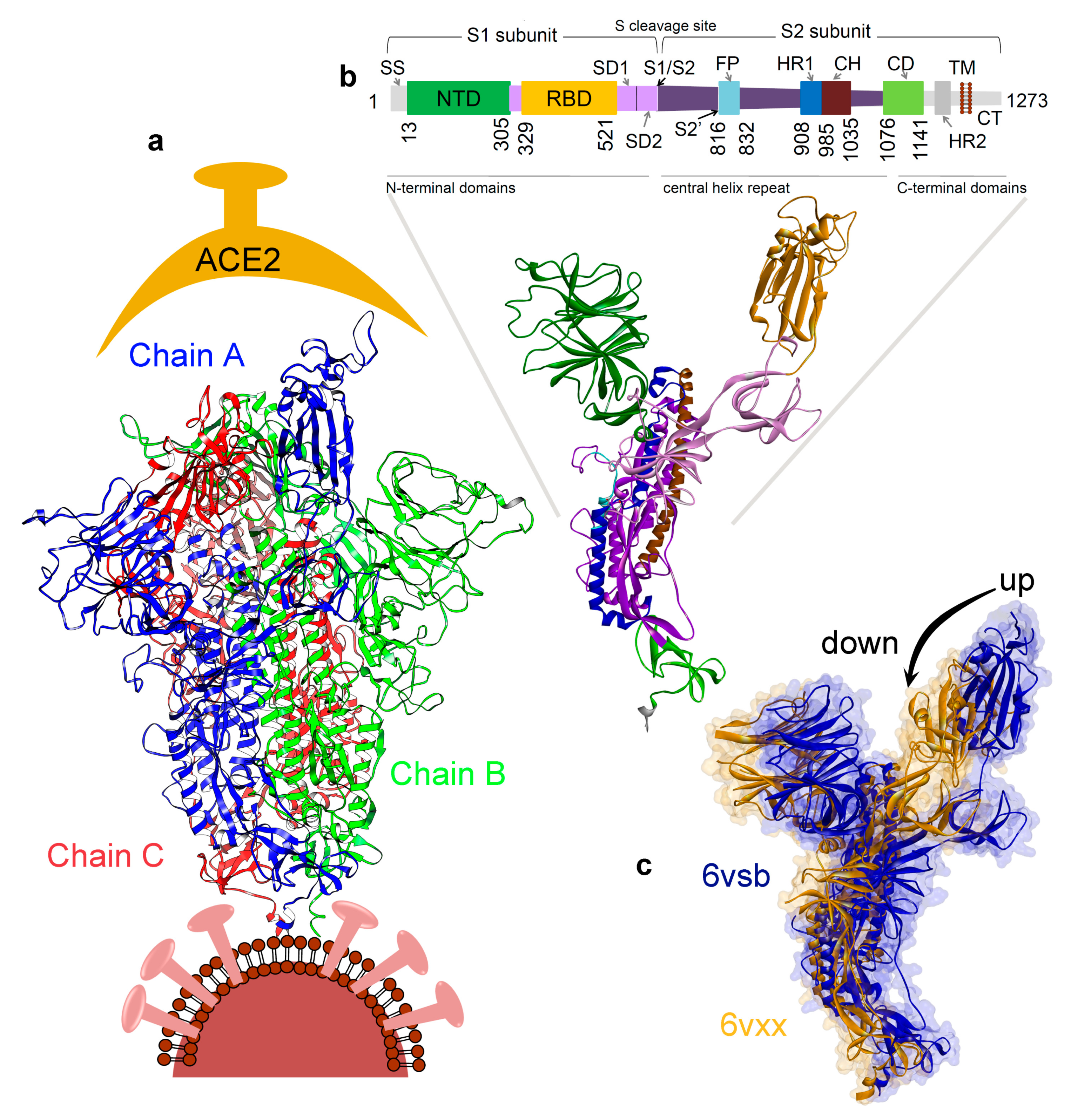
JCM | Free Full-Text | Highly Conserved Homotrimer Cavity Formed by the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein: A Novel Binding Site
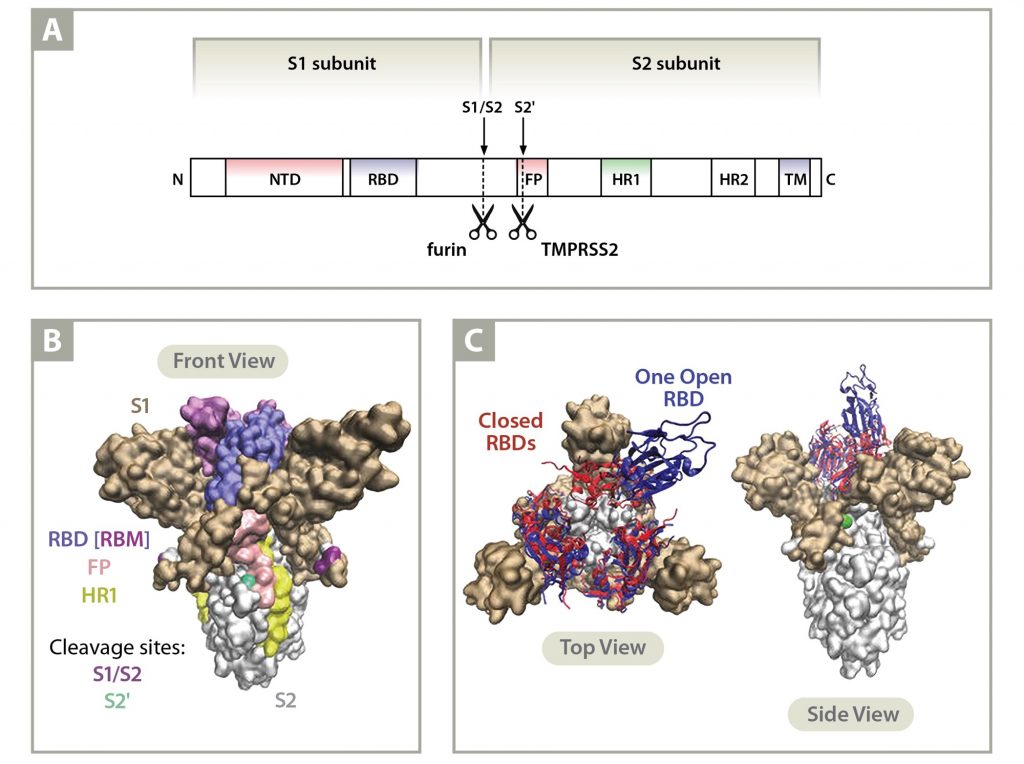
Implications of the Mutations in the Spike Protein of the Omicron Variant of Concern (VoC) of SARS-CoV-2 – Signature Science

Exploring the genomic and proteomic variations of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein: a computational biology approach | bioRxiv